Introduction

In Ghana, the relationship between the President and the Attorney General is fundamental to the effective functioning of governance. The 1992 Constitution clearly delineates their roles, ensuring a balance between executive authority and the rule of law. This article explores their respective duties, the legal framework governing their interactions, and the principles ensuring accountability and independence.
The Role of the President of Ghana
The President of Ghana serves as the head of state, government, and commander-in-chief of the Ghana Armed Forces. As the nation’s chief executive, the President is charged with leading the government and enforcing laws enacted by Parliament.
Key Responsibilities of the President:
Execution of Laws:
- Ensures all enacted laws are implemented effectively (Article 58).
Appointments:
- Appoints ministers, including the Attorney General, with parliamentary approval (Article 70).
National Policy Leadership:
- Shapes the policies that drive the development agenda of the nation.
International Representation:
- Signs treaties and represents Ghana on the global stage.
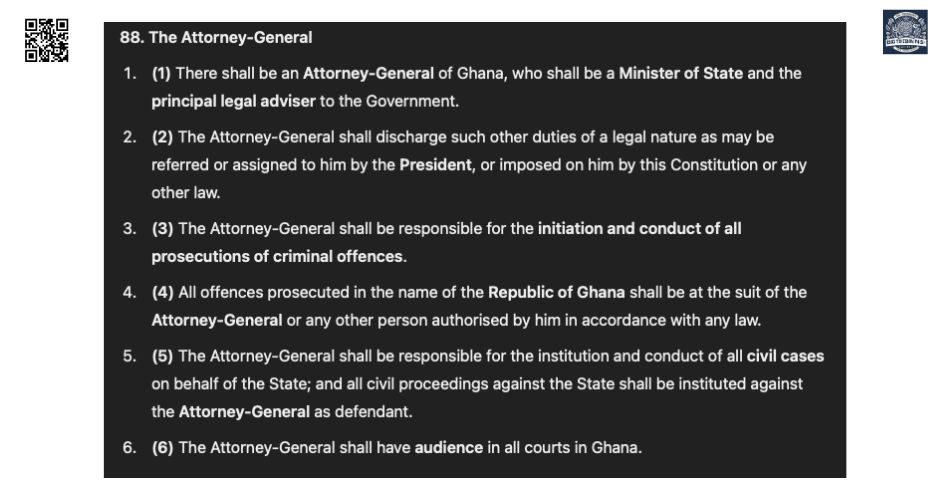
The Role of the Attorney General of Ghana

The Attorney General serves as the government’s principal legal advisor and is constitutionally mandated to oversee the initiation and conduct of criminal prosecutions. As the head of the Ministry of Justice, the Attorney General ensures that government actions align with legal principles.
Key Responsibilities of the Attorney General:
Legal Advisor:
- Provides advice to the President and government agencies on legal matters (Article 88).
Prosecutions:
- Initiates and oversees all criminal prosecutions in Ghana.
State Representation:
- Represents the state in civil proceedings and other legal matters.
Legislative Drafting:
- Oversees the preparation of bills and statutory instruments for Parliament.
Relationship Between the President and the Attorney General
The President and the Attorney General operate within a relationship of mutual accountability and respect for constitutional boundaries. While the Attorney General is a minister of state appointed by the President, their role demands a level of independence to ensure adherence to the rule of law.
Key Aspects of Their Relationship:
Appointing Authority:
- The President appoints the Attorney General, who serves as part of the executive.
Accountability:
- The Attorney General is accountable to the President but must independently exercise prosecutorial powers to uphold justice.
Collaboration on Policy:
- The Attorney General supports the President in shaping legally sound national policies.
Legal Framework Governing Their Duties
The 1992 Constitution provides the foundational framework for the roles of the President and the Attorney General.
Key provisions include:
Article 58:
- Outlines the executive powers of the President.

Article 70:
- Governs the appointment of ministers, including the Attorney General.

Article 88:
- Defines the powers and duties of the Attorney General.
NB: Additionally, statutes such as the Criminal Procedure Code and the Legal Profession Act offer specific guidance on operational aspects of their roles.
Ensuring Checks and Balances
To prevent misuse of power, the Constitution incorporates mechanisms that ensure checks and balances between the President and the Attorney General:
Judicial Oversight:
- The judiciary ensures that both the President and the Attorney General operate within legal boundaries.
Parliamentary Scrutiny:
- Parliament oversees appointments and can question the actions of the Attorney General.
Rule of Law:
- Both offices are bound by the principle that no one is above the law.
Conclusion
The relationship between Ghana’s President and Attorney General exemplifies the interplay of power and responsibility within a constitutional democracy. While the President wields executive authority, the Attorney General safeguards the legal integrity of governance. Together, their roles underscore the importance of accountability, independence, and adherence to the rule of law in achieving national development.
FAQs:
1. What is the role of Ghana’s President in governance?
- The President of Ghana is the head of state, head of government, and commander-in-chief of the armed forces. They are responsible for executing laws, shaping national policies, appointing key government officials, and representing Ghana in international relations.
2. Who appoints the Attorney General in Ghana?
- The Attorney General is appointed by the President of Ghana, with the prior approval of Parliament, as stipulated in Article 70 of the 1992 Constitution.
3. What are the main duties of Ghana’s Attorney General?
- The Attorney General acts as the principal legal advisor to the government, oversees the prosecution of crimes, represents the state in legal matters, and drafts legislation for Parliament.
4. How does the Attorney General maintain independence in prosecutions?
- Though part of the executive, the Attorney General is constitutionally mandated to act independently in legal prosecutions to ensure the rule of law and impartiality.
5. Can the President influence the Attorney General’s legal decisions?
- While the Attorney General is accountable to the President as a minister of state, they must adhere to constitutional and legal principles, ensuring that decisions are based on law and not political influence.
6. What laws govern the roles of the President and Attorney General in Ghana?
- The roles are primarily governed by the 1992 Constitution, particularly Articles 58, 70, and 88, alongside other statutes like the Legal Profession Act and the Criminal Procedure Code.
7. What is the relationship between Ghana’s President and the Attorney General?
- The Attorney General advises the President on legal matters, represents the state in legal proceedings, and ensures government actions are legally sound. However, they are expected to operate independently in prosecutorial decisions.
8. How does the Constitution ensure checks and balances between the President and the Attorney General?
- The Constitution mandates the Attorney General to adhere to legal standards, while Parliament and the judiciary provide oversight to prevent overreach or misuse of power by either party.

