Bernard Quayson (IT-Specialist)

REVIEW
The National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) is one of the best policies ever implemented in the history of Ghana, since independence. Though it might not have fully served its purpose, millions of Ghanaian citizens have benefitted immensely under this policy. Initially, Ghana operated a cost-recovery health delivery system known informally as “Cash-and-Carry” system since 1985, whereby citizens are required to pay up-front for health services at government clinics and hospitals.
This has, however, pushed health care far beyond the reach of ordinary Ghanaians. NHIS is the solution for the health care sector and the only viable alternative to the outdated and rigid system of ‘Cash-and-Carry’. At least the government’s objective to increase access to the formal health care sector through insurance has partially been achieved.
WHAT IS CBHIS?
The Early Age
Health care financing in Ghana started with a tax funded system that provided free public health services to all after independence. Low user fees were initially established for hospital services to discourage unnecessary use. So, government spending on health through the 1970s and 1980s led to shortages of medicines and supplies, and worsening quality of care.
Ex-President John J. Rawlings administration (NDC) in 1983, increased user fees for public health care services, and that is what became known as the “Cash-and-Carry“. This user fee system by Rawlings did well to improve operating revenues, but was poorly regulated and became difficult for vulnerable or poor citizens to access.
Ghana began to seek other ways of financing health care, including NGO-initiated community-based health insurance schemes (CBHIS). This type of insurance scheme targeted only about 1% of the population with limited benefit packages. So the system of user fees (Cash-and-Carry) remained the predominant or regular means of paying for health care.
NHIS INTRODUCTORY
The unpopular ‘Cash-and-Carry‘ system became a political issue, and the main opposition party (New Patriotic Party-NPP) at the time called for its abolishment in their manifestos and campaigns. Maybe that won the NPP the presidential and Parliamentary elections in 2000.
The National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) was established under Act 650 of August 2003 by the Government of Ghana, led by ex-president John Agyekum Kufuor’s administration (NPP). it was two years after he was voted into power as president of Ghana.
Purpose of NHIS
This program was a form of national (nation-wide) health insurance established to provide access and financial coverage for basic health care services to Ghanaian citizens. In other words, to increase affordability and utilization of health services in general. With this insurance, the cost of seeking professional treatment decreases.
Mode of NHIS Operations.
Like all insurance schemes, different types of premiums are available under the country’s NHIS policy. The premiums are grouped according to the level of income.
THE NHIA
The National Health Insurance Authority (NHIA) is the body corporate established under the National Insurance Act 2003, Act 650, to license and regulate District-level Mutual Health Insurance Schemes (DMHISs) as well as other schemes allowed under the Act. NHIA was commissioned to secure the NHIS policy that ensures access to basic health care services to all residents.
NHIS FUNDINGS
NHIS is financed from four main sources.
- 2.5% of Value-added tax on goods and services (National Health Insurance Levy- NHIL).
- An earmarked portion of social security taxes from formal sector workers.
- Premiums.
- Funds from investment returns, parliament, or donors.
NB: The 2.5% tax on goods and services (NHIL) is by far the biggest source of funding, comprising about 70% of revenues. Social security tax account for 23%, premiums for about 5%, and other funds for the remaining 2%.
Minimum Health Care Benefits under NHIS
- Outpatient services
- Inpatient services
- Emergencies
Exemptions
- 18 conditions are exempted from the package. this includes cancer, other than breast and cervical cancer.
Public Health programs
- Immunisation
- Family planning
- In-patient and out-patient treatment for mental illness
- Treatment of Tuberculosis, Onchocerciasis, Burull Ulcer, Trachoma; and
- Confirmatory HIV test on Aids patients.
Registration of NHIS
Section 31 of Act 650 reads;
- “A person resident in Ghana other than a member of Armed forces of Ghana and the police service shall belong to a health insurance scheme licensed under this Act.”
- A person residing in a district who is not a member of a private health insurance scheme registered under this Act, shall apply to be enrolled as a member of the district mutual health insurance scheme in the relevant district. However, enrollment is de facto voluntary because there is no penalty for failing to enroll, and individuals or households are not automatically enrolled.
Paperwork Registration
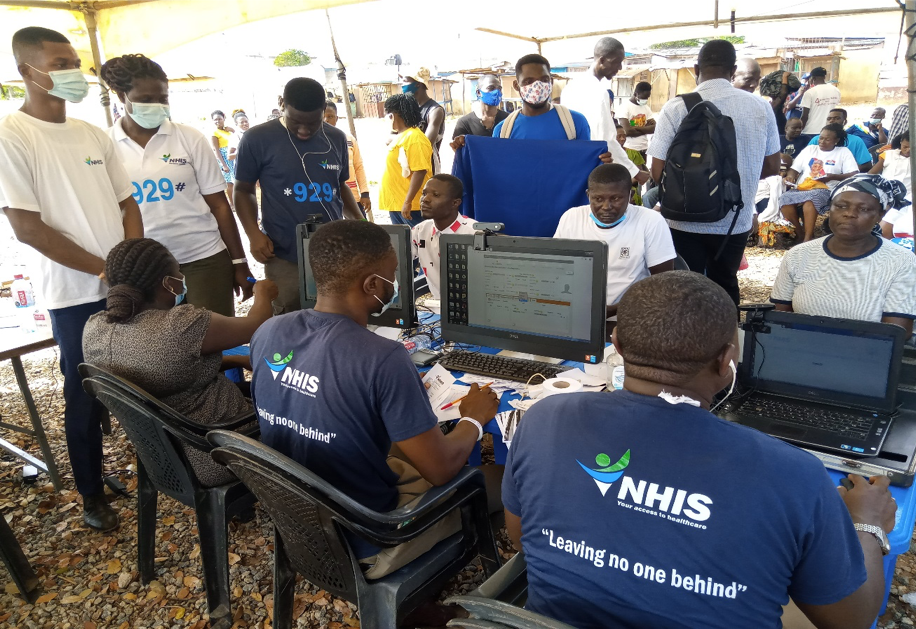

Ghanaians generally must go in-person to the DMHIS office to complete the paperwork registration.
A small registration fee meant to cover the photo ID and administrative expenses of registration shall be paid.
Registration requires a subscription to a premium according to a person’s income or wealth, ranging from GH¢ 7.2 for the “very poor” to GH¢ 48 for the “very Rich”.
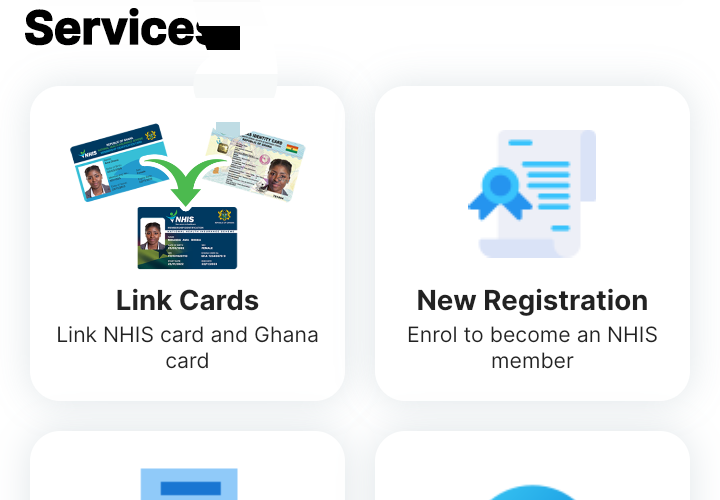
Self Registration with NHIS Mobile App
1. Download and install MyNHIS App from your phone's Playstore.
2. Open or launch the App.

3. Tap or click on New Registration

4. Tap or click Next to continue

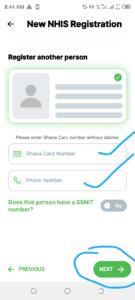
5. Provide Ghana card number and phone number of the person you're registering and tap Next.
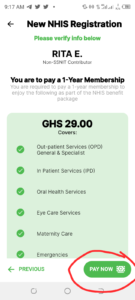
6. Tap 'Pay Now' to pay a 1-year membership premium of GH¢ 29.00
7. Choose your mode of payment.

8. Provide the phone number or information of your wallet.
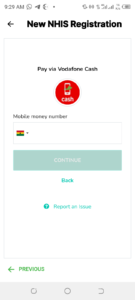
9. Enter the 4-digit OTP number sent to your phone number or email.

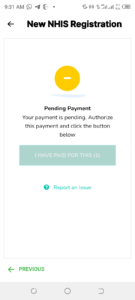
10. Enter your four-digit mobile wallet pin to authorize payment.
References:
- National Health Insurance Authority of Ghana
- Ministry of health, Ghana
- The World Bank Group
- Wikipedia.com
- Joint Learning Network
- The New Humanitarian